- August 7, 2017
- Posted by: cyberanalyst
- Category: Blog, CISSP, Consulting, Cyber-security and Ethical Hacking Training, Development, Digital Marketing, Others, Project and Research Nigeria, Softwares, Technologies, Website Design Service Abuja, Website Design Training, Website Hosting
An IT audit is an audit that deals with the review and evaluation of all automated and non-automated information processing systems and all the interfaces that it encompasses. It also includes setting up management controls for information technology and infrastructures.
The elementary function of IT audits includes, evaluation of systems that are already in place to guard the organization’s information. It looks into the ability of an organization to protect its assets as well as be able to legitimately and adequately give out information to authorized parties.
The process of planning IT audits involves two key steps
- Gathering information and planning
- Gaining an understanding of the already existing internal control structures
| Want to start an eBusiness and Grow it Globally with free IT, Legal, Internet Discounts,3 Months SME Startup Course, ePayment Integration, Biz Development Services, Free Website, Free SMS Units/Portal all done for you within 30 Days?
Start Here>> Click >>> Start a Digital Business in Nigeria
Many organizations are gradually phasing towards the approach of risk-based audits which is used for risk assessment and to help the IT auditor to decide on whether to carry out a compliance and substantive test. The risk based approach involves the IT auditors relying on the internal and operational controls and also the knowledge of the organization involved.
 However, this type of decision as regards risk assessment can go a long way to relate the profits analysis of the control to the risk.
However, this type of decision as regards risk assessment can go a long way to relate the profits analysis of the control to the risk.
These are the 5 aspects that an IT auditor needs to identify when gathering information:
- Good knowledge of the business and industry
- Previous results obtained from all the years
- Recent financial data
- Already existing standards and policies
- Inherent risk assessments
Inherent risk here refers to the risk that there is an error that could be a function of combined errors that are encountered during this audit assuming there are no controls in place.
Once the auditor has gathered relevant information and has an understanding of the control, then they are ready to start planning or select areas that need auditing.
Why is it important to do an IT Audit?
Hardly will you find an organization in recent times that is not IT driven. A lot of organisations today are investing huge amounts of cash on their IT infrastructure because they have come to realize the tremendous importance of using IT in their business services and operations. As a result of this, they need to always make sure that their IT systems are very secure, very reliable and is not susceptible or vulnerable to any form of cyber attacks.
The importance if an IT audit can never be over emphasized because it provides the assurance that the IT systems deployed by the organization is well protected, is available at all times, properly managed to get the required results and that it gives out reliable information to users. Many people use and rely on IT without knowing how it works and that a computer can make errors repeatedly and incurring extensive damages than a human being can. An IT audit is also very important in reducing risk of data leakage, data losses, service disruptions and ill-management of an IT infrastructure.
The Objectives of an IT audit
The objectives of an IT audit often focus on substantiating that the existing internal controls and are functioning as expected in order to minimize business risk. The objectives include
- Assuring compliance with legal and regulatory standards
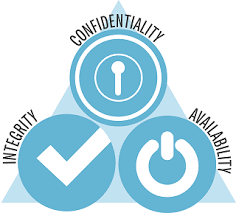
- Ensuring confidentiality
- Ensuring Integrity
- Improving availability of information systems
Confidentiality here relates to information security and refers to protecting information from being disclosed to unauthorized persons or parties. This means that information such as personal credentials, trade secrets, bank account statements are kept confidential and protecting this information plays a major role in information security.
The fact that information is valuable only when it has not been tampered with gives way to data integrity such that information is not modified by an unauthorized party. If information is inappropriately altered, it could prove costly for example, a transaction of 1000naira can be altered to 10,000naira. Making sure data is protected from being tampered with is a core aspect of information security.
Availability here means that information is made available to authorized individuals whenever it is needed. Unfortunately, the act of denying rights to resources to rightful users has been in on the rise lately. An information systems audit will therefore ensure confidentiality of an organizations data, data integrity and availability of resources. An IT audit therefore oversees the organizations IT systems, its operations and management processes.
The reliability of data from an IT system can as well have huge impact on the financial statements of an organization. There an IT audit must be able to
- Check for instances of excesses, gross inefficiencies, extravagance which has to do with wastage of resources in the management of IT systems
- Ensure that there is a high level of compliance with government laws as applicable to the IT system.
Types of IT audits
Different bodies and authorities have developed their views to distinguish the types of IT audits. Goodman and Lawless have outlined three systematic approaches to perform IT audits

- Technological Innovation Process Audit: This audit type attempts to construct a risk profile for already existing as well as new projects. It assesses the length, depth and presence of the technologies used by the company and how it relates to the relevant markets. It also looks into the way each project is organized, the structure of industry as regards its projects, products etc.
- Technological position audit: This audit type deals with the technologies that the business has on ground and what it needs to add to it. Technologies can be categorized into
- Base
- Key
- Pacing
- Emerging
- Innovative Comparison Audit: This audit deals with the analysis of the innovative capabilities of the organization being audited when compared to its competitors and rivals. The company’s research and development facilities as well as its track record of producing new products will be examined.
Other authorities have also categorized IT audits in 5 spectrum
- Information Processing Facilities: It is focused on verifying the processing ability of the facility and if it is designed under normal and disruptive conditions to process applications in a timely, accurate and efficient way.
- Systems and Applications: It is focused on verifying systems activity are controlled appropriately, efficiently and adequately in order to ensure its output at all levels are valid, reliable, and timely. This audit type forms a sub-type that focuses on business IT systems and also focuses on financial auditors.
- Management of IT and Enterprise Architecture: IT focuses on verifying that organizational structure and procedure that ensures a controlled and efficient information processing environment is developed by the IT management.
- Systems Development: This audit verifies the systems that are under the process of development meet the requirements and objectives of the organization. It also ensures that the systems are developed in line with generally accepted policies and standards for systems development.
- Client/Server, Intranets, extranets and Telecommunications: This audit verifies that the controls for telecommunications are in place both the client and the server ends as well as the network that connects both the clients and servers.
Types of Auditors
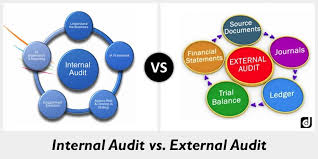
- Internal Auditor: This auditor usually performs internal accounts auditing as well as IS audits.

- External Auditor: This auditor reviews the findings and inputs, processes and outputs of the information systems made by the internal auditor.
Types of Audits
- Internal Audits: As explained above, an internal audit considers all the potential controls and hazards in an information system. It takes care if issues like operations, data, data integrity, security, privacy, software applications, productivity, expenditures, cost control and budgets. The auditor works with guidelines such as Information systems audit and control association which are available to make their job patterned.
- External Audits: This audits buttresses on information obtained from internal audits on information systems. External audit is performed by an certified information systems audit expert.
IT Audit Strategies
- We’ll discuss two areas here but first one must be able to determine if it is a compliance or substantive testing. The next thing to consider is how to go about gathering evidences to enable one perform application audits and make reports to the management.
What is substantive and Compliance Testing?
- Compliance testing involves gathering evidence to test if an organization is following the control procedures. For example, If an organization has a control procedure that says all application changes have to pass through a change control, an IT auditor will have to get the current running configurations of the router as well as the configuration file. After he does this, he can then run a file to compare the differences and use the result of the differences to look for a supporting change control documentation.

- Substantive Testing involves gathering evidence that enables one evaluate the data integrity of individual data and other information. For example, If an organization has a policy that has to do with backup tapes in storage locations offsite which includes three generations (Grandfather, father and son), then the IS auditor has to take physical inventory of the tapes in an offsite storage location as well. After this he can then compare it with the organizations inventory and also making sure the three generations are involved and are available at the time of the audit.
- The thing to discuss on is How to get the evidence that can help you audit the application and deliver a report to management. A few things you can review are;
- Review the IT organizational structure
- Review the IT policies and procedures
- Review the IT standards
- Review the IT documentations
- Review the organizations BIA
- Take time to interview employees
- Observe the employee’s performance
- Test controls and examine necessary incorporated entities
- Draft out a set of questionnaires
- Whether there is a thorough documentation of approved IS audit guideline?
- Whether IS audit guidelines are consistent with the security policy?
- Whether responsibilities for the IT audit has been assigned to a separate unit that is independent of the IT department?
- Whether periodic external IS audit is carried out?
- Whether independent security audit is conducted periodically?
- Whether contingency planning, insurance of assets, data integrity etc. are made part of External audit?
- Whether vulnerability and penetration testing were made part of external audit?
- Whether the major concerns brought out by previous Audit Reports have been highlighted and brought to the notice of the Top Management?
- Whether necessary corrective action has been taken to the satisfaction of the Management?
- Whether the facilities for conducting trainings which will enable IS audit teams to conduct the audit process effectively?
- Whether IS audit team is encouraged to keep themselves updated?
- Whether IS auditors exchange their views and share their experiences internally?
Operations is modern organizations are increasing dependent on IT, this is why IT audits are used to make sure that all information-related controls and methods are functioning properly. Most of all the companies if not all are IT driven and not enough awareness has been made on auditing of IT infrastructure the reason for this write up. If you’re in search of a professional firm to audit your organization, look no more as soutech web consults which is the number one IT consulting firms offers in Nigeria offers this service. Subscribe to us for your auditing and all types of IT-related issues.
| Want to start an eBusiness and Grow it Globally with free IT, Legal, Internet Discounts,3 Months SME Startup Course, ePayment Integration, Biz Development Services, Free Website, Free SMS Units/Portal all done for you within 30 Days?
Start Here>> Click >>> Start a Digital Business in Nigeria