- November 19, 2019
- Posted by: SouTech Team
- Category: Blog, CEH, CISSP, Consulting, Cyber-security and Ethical Hacking Training
Nmap (“Network Mapper”) is a free and open source (license) utility for network discovery and security auditing. Many systems and network administrators also find it useful for tasks such as network inventory, managing service upgrade schedules, and monitoring host or service uptime. Nmap uses raw IP packets in novel ways to determine what hosts are available on the network, what services (application name and version) those hosts are offering, what operating systems (and OS versions) they are running, what type of packet filters/firewalls are in use, and dozens of other characteristics. It was designed to rapidly scan large networks, but works fine against single hosts. Nmap runs on all major computer operating systems, and official binary packages are available for Linux, Windows, and Mac OS X. In addition to the classic command-line Nmap executable, the Nmap suite includes an advanced GUI and results viewer (Zenmap), a flexible data transfer, redirection, and debugging tool (Ncat), a utility for comparing scan results (Ndiff), and a packet generation and response analysis tool (Nping).
Nmap was named “Security Product of the Year” by Linux Journal, Info World, LinuxQuestions.Org, and Codetalker Digest. It was even featured in twelve movies, including The Matrix Reloaded, Die Hard 4, Girl With the Dragon Tattoo, and The Bourne Ultimatum.
https://nmap.org/download.html
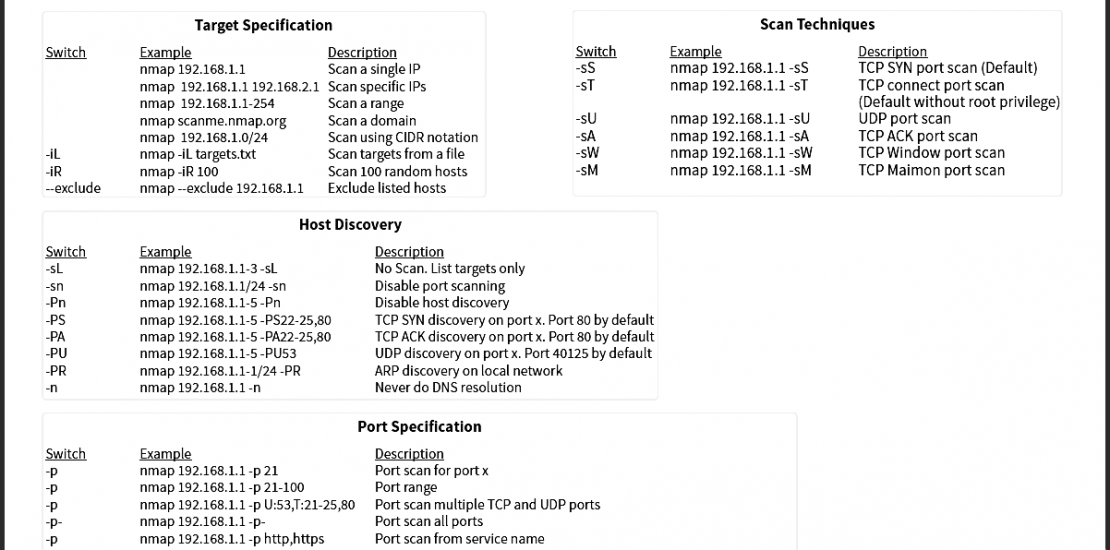
Target Specification
|
Switch |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
nmap 192.168.1.1 |
Scan a single IP |
|
|
nmap 192.168.1.1 192.168.2.1 |
Scan specific IPs |
|
|
nmap 192.168.1.1-254 |
Scan a range |
|
|
nmap scanme.nmap.org |
Scan a domain |
|
|
nmap 192.168.1.0/24 |
Scan using CIDR notation |
|
|
-iL |
nmap -iL targets.txt |
Scan targets from a file |
|
-iR |
nmap -iR 100 |
Scan 100 random hosts |
|
–exclude |
nmap –exclude 192.168.1.1 |
Exclude listed hosts |
Scan Techniques
|
Switch |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
-sS |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sS |
TCP SYN port scan (Default) |
|
-sT |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sT |
TCP connect port scan |
|
-sU |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sU |
UDP port scan |
|
-sA |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sA |
TCP ACK port scan |
|
-sW |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sW |
TCP Window port scan |
|
-sM |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sM |
TCP Maimon port scan |
Host Discovery
|
Switch |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
-sL |
nmap 192.168.1.1-3 -sL |
No Scan. List targets only |
|
-sn |
nmap 192.168.1.1/24 -sn |
Disable port scanning. Host discovery only. |
|
-Pn |
nmap 192.168.1.1-5 -Pn |
Disable host discovery. Port scan only. |
|
-PS |
nmap 192.168.1.1-5 -PS22-25,80 |
TCP SYN discovery on port x. Port 80 by default |
|
-PA |
nmap 192.168.1.1-5 -PA22-25,80 |
TCP ACK discovery on port x. Port 80 by default |
|
-PU |
nmap 192.168.1.1-5 -PU53 |
UDP discovery on port x. Port 40125 by default |
|
-PR |
nmap 192.168.1.1-1/24 -PR |
ARP discovery on local network |
|
-n |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -n |
Never do DNS resolution |
Port Specification
|
Switch |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
-p |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -p 21 |
Port scan for port x |
|
-p |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -p 21-100 |
Port range |
|
-p |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -p U:53,T:21-25,80 |
Port scan multiple TCP and UDP ports |
|
-p- |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -p- |
Port scan all ports |
|
-p |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -p http,https |
Port scan from service name |
|
-F |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -F |
Fast port scan (100 ports) |
|
–top-ports |
nmap 192.168.1.1 –top-ports 2000 |
Port scan the top x ports |
|
-p-65535 |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -p-65535 |
Leaving off initial port in range |
|
-p0- |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -p0- |
Leaving off end port in range makes the scan go through to port 65535 |
Service and Version Detection
|
Switch |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
-sV |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sV |
Attempts to determine the version of the service running on port |
|
-sV –version-intensity |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sV –version-intensity 8 |
Intensity level 0 to 9. Higher number increases possibility of correctness |
|
-sV –version-light |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sV –version-light |
Enable light mode. Lower possibility of correctness. Faster |
|
-sV –version-all |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sV –version-all |
Enable intensity level 9. Higher possibility of correctness. Slower |
|
-A |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -A |
Enables OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute |
OS Detection
|
Switch |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
-O |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -O |
Remote OS detection using TCP/IP |
|
-O –osscan-limit |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -O –osscan-limit |
If at least one open and one closed |
|
-O –osscan-guess |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -O –osscan-guess |
Makes Nmap guess more aggressively |
|
-O –max-os-tries |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -O –max-os-tries 1 |
Set the maximum number x of OS |
|
-A |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -A |
Enables OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute |
Timing and Performance
|
Switch |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
-T0 |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -T0 |
Paranoid (0) Intrusion Detection |
|
-T1 |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -T1 |
Sneaky (1) Intrusion Detection System |
|
-T2 |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -T2 |
Polite (2) slows down the scan to use |
|
-T3 |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -T3 |
Normal (3) which is default speed |
|
-T4 |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -T4 |
Aggressive (4) speeds scans; assumes |
|
-T5 |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -T5 |
Insane (5) speeds scan; assumes you |
|
Switch |
Example input |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
–host-timeout <time> |
1s; 4m; 2h |
Give up on target after this long |
|
–min-rtt-timeout/max-rtt-timeout/initial-rtt-timeout <time> |
1s; 4m; 2h |
Specifies probe round trip time |
|
–min-hostgroup/max-hostgroup <size<size> |
50; 1024 |
Parallel host scan group |
|
–min-parallelism/max-parallelism <numprobes> |
10; 1 |
Probe parallelization |
|
–scan-delay/–max-scan-delay <time> |
20ms; 2s; 4m; 5h |
Adjust delay between probes |
|
–max-retries <tries> |
3 |
Specify the maximum number |
|
–min-rate <number> |
100 |
Send packets no slower than <numberr> per second |
|
–max-rate <number> |
100 |
Send packets no faster than <number> per second |
NSE Scripts
|
Switch |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
-sC |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sC |
Scan with default NSE scripts. Considered useful for discovery and safe |
|
–script default |
nmap 192.168.1.1 –script default |
Scan with default NSE scripts. Considered useful for discovery and safe |
|
–script |
nmap 192.168.1.1 –script=banner |
Scan with a single script. Example banner |
|
–script |
nmap 192.168.1.1 –script=http* |
Scan with a wildcard. Example http |
|
–script |
nmap 192.168.1.1 –script=http,banner |
Scan with two scripts. Example http and banner |
|
–script |
nmap 192.168.1.1 –script “not intrusive” |
Scan default, but remove intrusive scripts |
|
–script-args |
nmap –script snmp-sysdescr –script-args snmpcommunity=admin 192.168.1.1 |
NSE script with arguments |
Useful NSE Script Examples
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
nmap -Pn –script=http-sitemap-generator scanme.nmap.org |
http site map generator |
|
nmap -n -Pn -p 80 –open -sV -vvv –script banner,http-title -iR 1000 |
Fast search for random web servers |
|
nmap -Pn –script=dns-brute domain.com |
Brute forces DNS hostnames guessing subdomains |
|
nmap -n -Pn -vv -O -sV –script smb-enum*,smb-ls,smb-mbenum,smb-os-discovery,smb-s*,smb-vuln*,smbv2* -vv 192.168.1.1 |
Safe SMB scripts to run |
|
nmap –script whois* domain.com |
Whois query |
|
nmap -p80 –script http-unsafe-output-escaping scanme.nmap.org |
Detect cross site scripting vulnerabilities |
|
nmap -p80 –script http-sql-injection scanme.nmap.org |
Check for SQL injections |
Firewall / IDS Evasion and Spoofing
|
Switch |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
-f |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -f |
Requested scan (including ping scans) use tiny fragmented IP packets. Harder for packet filters |
|
–mtu |
nmap 192.168.1.1 –mtu 32 |
Set your own offset size |
|
-D |
nmap -D 192.168.1.101,192.168.1.102, |
Send scans from spoofed IPs |
|
-D |
nmap -D decoy-ip1,decoy-ip2,your-own-ip,decoy-ip3,decoy-ip4 remote-host-ip |
Above example explained |
|
-S |
nmap -S www.microsoft.com www.facebook.com |
Scan Facebook from Microsoft (-e eth0 -Pn may be required) |
|
-g |
nmap -g 53 192.168.1.1 |
Use given source port number |
|
–proxies |
nmap –proxies http://192.168.1.1:8080, http://192.168.1.2:8080 192.168.1.1 |
Relay connections through HTTP/SOCKS4 proxies |
|
–data-length |
nmap –data-length 200 192.168.1.1 |
Appends random data to sent packets |
Example IDS Evasion command
nmap -f -t 0 -n -Pn –data-length 200 -D 192.168.1.101,192.168.1.102,192.168.1.103,192.168.1.23 192.168.1.1
Output
|
Switch |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
-oN |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -oN normal.file |
Normal output to the file normal.file |
|
-oX |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -oX xml.file |
XML output to the file xml.file |
|
-oG |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -oG grep.file |
Grepable output to the file grep.file |
|
-oA |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -oA results |
Output in the three major formats at once |
|
-oG – |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -oG – |
Grepable output to screen. -oN -, -oX – also usable |
|
–append-output |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -oN file.file –append-output |
Append a scan to a previous scan file |
|
-v |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -v |
Increase the verbosity level (use -vv or more for greater effect) |
|
-d |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -d |
Increase debugging level (use -dd or more for greater effect) |
|
–reason |
nmap 192.168.1.1 –reason |
Display the reason a port is in a particular state, same output as -vv |
|
–open |
nmap 192.168.1.1 –open |
Only show open (or possibly open) ports |
|
–packet-trace |
nmap 192.168.1.1 -T4 –packet-trace |
Show all packets sent and received |
|
–iflist |
nmap –iflist |
Shows the host interfaces and routes |
|
–resume |
nmap –resume results.file |
Resume a scan |
Helpful Nmap Output examples
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
nmap -p80 -sV -oG – –open 192.168.1.1/24 | grep open |
Scan for web servers and grep to show which IPs are running web servers |
|
nmap -iR 10 -n -oX out.xml | grep “Nmap” | cut -d ” ” -f5 > live-hosts.txt |
Generate a list of the IPs of live hosts |
|
nmap -iR 10 -n -oX out2.xml | grep “Nmap” | cut -d ” ” -f5 >> live-hosts.txt |
Append IP to the list of live hosts |
|
ndiff scanl.xml scan2.xml |
Compare output from nmap using the ndif |
|
xsltproc nmap.xml -o nmap.html |
Convert nmap xml files to html files |
|
grep ” open ” results.nmap | sed -r ‘s/ +/ /g’ | sort | uniq -c | sort -rn | less |
Reverse sorted list of how often ports turn up |
Miscellaneous Options
|
Switch |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
-6 |
nmap -6 2607:f0d0:1002:51::4 |
Enable IPv6 scanning |
|
-h |
nmap -h |
nmap help screen |
Other Useful Nmap Commands
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
nmap -iR 10 -PS22-25,80,113,1050,35000 -v -sn |
Discovery only on ports x, no port scan |
|
nmap 192.168.1.1-1/24 -PR -sn -vv |
Arp discovery only on local network, no port scan |
|
nmap -iR 10 -sn -traceroute |
Traceroute to random targets, no port scan |
|
nmap 192.168.1.1-50 -sL –dns-server 192.168.1.1 |
Query the Internal DNS for hosts, list targets only |
More information and fact sheets download
 Loading...
Loading...
Want to learn? https://www.soutechventures.com/ilearn/courses.php See course details- over 20 Tech Skills

Get 80% Discount when you chat up (234) 8034121380 via WhatsApp
Get Cashback when you refer your friends, Let’s get started!!!